Currently, some of the downstream market demands are reaching saturation, but the overall trend is still quite positive.
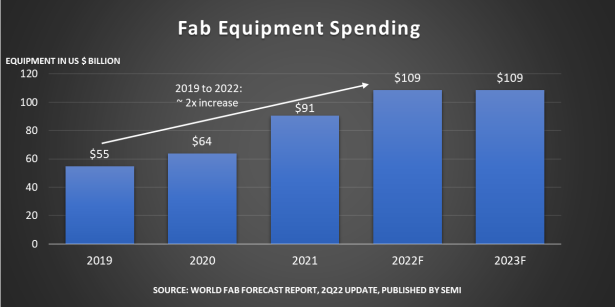
On a higher level, SEMI, in its latest World Fab Forecast report, provides data showing that the investment in front-end manufacturing equipment for fabs is expected to reach $109 billion in 2022, setting a new historical record and the first time surpassing $100 billion. The year-on-year growth for 2022 is 20%, which, although slightly lower than the 42% increase in 2021, still suggests that 2022 will mark three consecutive years of rapid growth.
SEMI President and CEO Ajit Manocha stated, "This record-breaking investment underscores the unprecedented and sustained growth in the industry," highlighting the significance of the $109 billion forecast. By examining data from SEMI, Gartner, and Counterpoint Research, we can better understand the current state of the semiconductor manufacturing (including foundries) market, which is helpful for predicting the future direction of the industry.
Manufacturing equipment investments continue to rise, with Taiwan leading
Focusing on semiconductor manufacturing equipment, SEMI’s report mentions that global fab equipment facilities will expand by 8% this year, compared to a 7% growth rate last year. SEMI expects the fab equipment market capacity to continue growing in 2023, with a projected growth of about 6%.
The last time an 8% year-over-year increase occurred was in 2010, when wafer monthly capacity reached 16 million units (equivalent to 200mm wafers). It is expected that by 2023, this figure will rise to 29 million wafers per month. In 2022, 85% of the spending on semiconductor manufacturing equipment will come from the capacity expansion of 158 fab plants and production lines.
Regionally, Taiwan will remain the largest spender on fab manufacturing equipment, with an investment of $34 billion, a 52% year-on-year growth. Following Taiwan is South Korea, with a 7% increase, totaling $25.5 billion. Mainland China, ranking third, is expected to see a 14% decline in fab equipment investment, totaling $17 billion, which is largely due to a significant drop following last year’s high growth.
Meanwhile, investments in Europe and the Middle East will reach a record $9.3 billion, an increase of 176%. The Americas are projected to see 13% and 19% growth in fab equipment investment for 2022 and 2023, respectively, reaching around $9.3 billion in 2023. SEMI forecasts favorable growth in Taiwan, South Korea, and Southeast Asia in 2023.
Top 10 Foundries
The investments in manufacturing equipment are predictable by region. In a recent semiconductor industry report by Gartner, the top 10 foundries in terms of revenue for 2021 were listed, though this doesn't cover the entire semiconductor manufacturing industry, it still provides a clear reflection of the current market status.
The top 10 foundries by revenue included TSMC, Samsung, UMC, GlobalFoundries, SMIC, PSMC, Shanghai Huahong Grace, Vanguard International Semiconductor, Tower Semiconductor, and Shanghai Huahong. Taiwan, mainland China, and South Korea are clearly the dominant players.
Even the slowest-growing foundry, Tower Semiconductor, saw a 19% revenue growth in 2021. Players like SMIC and GlobalFoundries saw revenue growth rates of over 35%. The fastest-growing companies were Samsung Foundry, PSMC, and Shanghai Huahong Grace, with growth rates of 66%, 74%, and 70%, respectively.
Gartner noted that Samsung Foundry’s growth was driven by Qualcomm’s 5G chips, Nvidia GPUs, Google’s TPUs, and the strong demand from the mining industry for mining cards. PSMC’s growth was attributed to DDI chips and some of their specialty processes. Shanghai Huahong Grace’s strong growth was largely due to the capacity increase at their Wuxi facility. Gartner also highlighted SMIC’s capacity growth in 14nm processes, which became a key factor in their revenue increase.
Despite these strong performances, no foundry is currently in a position to rival TSMC in terms of revenue. TSMC’s revenue in 2021 exceeded $50 billion, while none of the other top 9 foundries surpassed $10 billion. In total, the top 10 foundries’ combined revenue reached $100.2 billion, with an average growth rate of 31.3%, largely driven by TSMC.
Counterpoint Research recently released Q1 2022 revenue share data for foundries. The overall situation is similar to last year. TSMC's Q1 2022 report highlighted its growth driven by HPC, including clients like Apple, AMD, Nvidia, and more. It also noted that HPC has now overtaken the smartphone sector to become TSMC’s most profitable application.
Notably, the overall growth of foundries is closely tied to the rise in wafer average selling prices (ASP), which has been common in the current chip shortage environment. Many companies have seen significant performance growth during this period, with PSMC being one of the most representative examples.
Price trends for different processes
According to Counterpoint Research’s data, the process with the highest revenue share in Q1 2022 was the 7nm/6nm process, accounting for 18%. The main chips in this category include smartphone AP/SoC, tablet APUs, GPUs, and CPUs. The second-highest revenue came from 16/14/12nm processes (grouped together as they belong to the same process family), with major revenue from smartphone RF IC/4G SoC, wearable device processors, SSD controllers, and some PC-related ICs.
Gartner recently reported on the revenue growth of different processes in 2021. The fastest-growing process was undoubtedly 5nm, with a 198% market value increase compared to 2020. This is the primary process for flagship smartphone AP/SoC chips, as well as applications like Apple’s Mac chips. According to Gartner’s data, 7nm currently holds the largest revenue share among all processes, with a 17% year-on-year growth rate starting in 2021.
In 2021, processes like 28nm and 65nm saw relatively fast price increases, partly due to the large demand for MCU and other chips. For instance, 65nm process revenue grew by 48% in 2021 compared to 2020, revealing strong market demand.
Revenue from different processes depends on the foundries' investment levels. Gartner believes that the 28nm process currently has significant investment and that its supply capacity will increase substantially in the next few years. SMIC, for example, is planning to build 28nm factories in Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen. The trends for investments in various processes can help predict potential shortages or oversupply in the market.
As a cyclical industry, semiconductor manufacturing often experiences various shifts between supply and demand, with growth and decline following cyclical patterns. Semiconductor manufacturing’s response to market conditions tends to be slower. Given that demand is approaching saturation for many chip types, observing the semiconductor manufacturing market in 2023-2024 will reveal a different landscape.